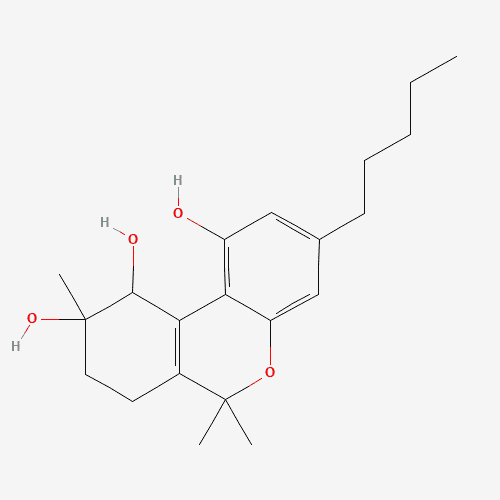
What is Cannabitriol?
CBT, short for cannabitriol, is a cannabinoid that was first isolated back in 1966. Cannabinoids are cannabis compounds produced by cannabis plants, including both hemp and marijuana. These compounds are called phytocannabinoids because they were originally created biologically within the cannabis plant. There are both major cannabinoids like CBD and THC, and minor cannabinoids like CBT, present in the plant. CBD offers very notable therapeutic effects, while what CBT offers is not quite known as of the time of this writing.
It is considered not only a natural cannabinoid, but also a metabolite of THC, when THC is oxidized. It is also present in many CBD extracts, as it helps to prevent crystalization of high CBD extract, a well known problem in the hemp CBD industry.
Cannabidiol (CBD) is the arguably the most well studied cannabinoid, and it’s also one of the most abundant cannabinoids found in cannabis. CBD is considered by many to be non-psychoactive, meaning it doesn’t cause a high. However, CBD does interact with other cannabinoids and terpenes, creating an entourage effect. This means that when you consume CBD, it interacts with other compounds in that you consume and that are within your body to create a synergistic effect of health benefits. CBT certainly plays a role in this compounding effect.
What Does CBT Do?
As mentioned earlier, CBT is a rare cannabinoid that is produced in small quantities, and not too much is known about the compound.
That said, what is know about its pharmacological is that CBT has shown that it may be effective at being an antiestrogen as well as an aromatase inhibitor.
There was also a study done by Mahmoud Elsohly that demonstrated that CBT might have some benefits to those who suffer from glaucoma.
Is CBT Psychoactive?
CBT is an active cannabinoid that is structurally similar to tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the main psychoactive compound found in cannabis. However, cannabitriol is only found in trace amounts in cannabis. With specialized breeding programs, it may be possible to create a genotype that would make it possible to extract CBT from cannabis in large enough quantities for scientists to study.
Looking like THC does not mean that it will act like THC, and the level of psychoactivity is not yet known. In fact, it is theorized that it could prevent some of the psychoactive effects of THC, kind of like CBD.
Isomers of CBT
10-Ο-Ethyl bis-nor cannabitriol
10-Ο-Ethyl cannabitriol isomer
7,8-Dehydro-10-Ο-ethylcannabitriol
Bis-nor cannabitriol
Bis-nor cannabitriol isomer
Isocannabitriol
Additional Resources
https://academic.oup.com/bbb/article-abstract/30/6/619/5976998?redirectedFrom=fulltext
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1253891/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/895385/