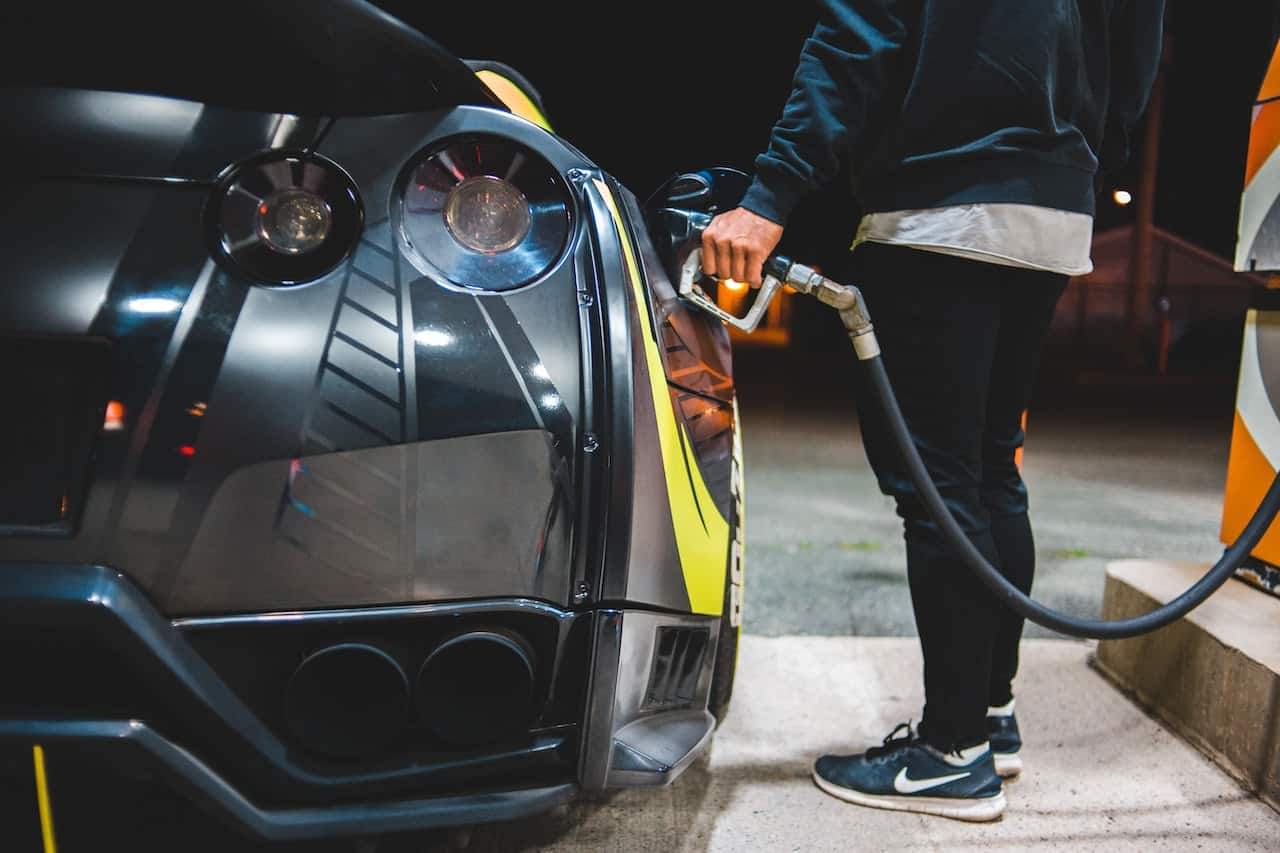

Benefits of Using Hemp for Biofuel
Definition of Hemp
Hemp, also known as industrial hemp, refers to a versatile and sustainable crop that is derived from the cannabis plant species.
Unlike its close relative, marijuana, hemp contains only trace amounts of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the psychoactive compound responsible for the “high” effect. Primarily cultivated for its fibrous stems and seeds, hemp has been used for centuries for various purposes, including clothing, rope, paper, and construction materials.
In recent years, hemp has gained attention as a potential renewable energy source and alternative fuel. Its rapid growth cycle, high cellulose content, and ability to grow on marginal lands make it an excellent alternative to fossil fuels. Hemp can be processed into various biofuels, such as hemp biodiesel, ethanol, and pellets, providing a renewable and environmentally friendly solution to reduce carbon dioxide emissions.
Furthermore, hemp seeds can be cold-pressed to extract hemp seed oil, which can also be used as a biofuel. With its numerous potential applications, hemp offers a promising pathway towards a greener and more sustainable future.
Definition of Biofuel
Biofuels are a type of fuel derived from renewable organic sources, such as crops or agricultural residues. They are considered a more sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to fossil fuels because they reduce carbon dioxide emissions and dependence on non-renewable resources.
In the context of using hemp for biofuel production, biofuels refer to fuels derived from hemp seeds, hemp oil, or hemp biomass. Hemp has gained attention as a promising source of biofuel due to its high energy potential and environmentally friendly properties.
Compared to traditional crops used for biofuel production, such as corn or soybeans, hemp offers several advantages. Hemp can be grown on marginal lands not suitable for food crops, reducing the competition for arable land. It has a higher yield per hectare and grows quickly, allowing for multiple harvests in a year. Additionally, hemp requires minimal use of pesticides and fertilizers, making it a more sustainable option.
Furthermore, hemp biofuel has a lower carbon footprint compared to fossil fuels, releasing less carbon dioxide when burned. Hemp can also be used in various forms, such as hemp pellets or hemp ethanol, making it a versatile renewable energy source.
The use of hemp for biofuel production offers significant environmentally friendly benefits. Its high energy potential, ability to grow on marginal lands, and lower carbon emissions make hemp an excellent alternative to traditional fuels. Harnessing the full potential of hemp as a biofuel source could contribute to a more sustainable and greener future.
How Hemp Can be Used for Biofuel Production
Hemp is a versatile and sustainable plant that has gained recognition as a potential source of biofuel. With its high cellulose content, hemp can be converted into ethanol through various fermentation processes, making it an excellent alternative energy source.
One of the primary fermentation processes used to convert hemp into biofuel is dry distillation. This process involves heating hemp biomass in the absence of oxygen, producing a rich, high-energy fuel known as hemp bioethanol. Another fermentation process commonly used is anaerobic digestion, where hemp biomass is broken down by bacteria in an oxygen-free environment, resulting in the production of methane gas, which can be used as fuel.
Using hemp for biofuel production offers several advantages. Unlike other crops like wheat and corn, hemp can be grown in lesser quality soil conditions, making it suitable for cultivation on marginal lands that are not suitable for food crops. Additionally, hemp’s sturdy fibers and natural oils make it safer to transport compared to other biofuel sources.
Furthermore, hemp biofuel is a cleaner and more sustainable alternative to traditional fuels. It releases fewer greenhouse gases and has a lower carbon footprint, contributing to the reduction of carbon dioxide emissions.
Hemp has great potential as a renewable energy source through its conversion into biofuel. Its versatility, ability to grow in various conditions, and cleaner energy production make it an attractive option for sustainable fuel alternatives.
Advantages of Using Hemp for Biofuel
Hemp is gaining recognition as a valuable resource for biofuel production due to its numerous advantages. First and foremost, hemp cultivation does not require fertile soils and can thrive on marginal lands that are unsuitable for food crops. This not only maximizes land use but also minimizes agricultural competition. Additionally, hemp’s strong fibers and natural oils make it a safe and efficient fuel source, easier to transport compared to other biomass materials.
In terms of sustainability, hemp biofuel offers significant benefits. It is a cleaner alternative to fossil fuels, releasing fewer greenhouse gases and contributing to the reduction of carbon dioxide emissions. Its cultivation also promotes carbon sequestration, as hemp plants absorb large amounts of CO2 during their growth cycle. Furthermore, hemp biofuel production helps in diversifying energy sources and reducing dependence on petroleum-based fuels, mitigating the negative environmental impacts associated with their extraction and combustion.
Another noteworthy advantage of hemp biofuel is its versatility. It can be produced through various processes such as dry distillation and anaerobic digestion, offering different fuel options like bioethanol and methane gas. Moreover, hemp has a high yield per hectare, producing a significant amount of biofuel per unit of land. This makes it a promising candidate for large-scale biofuel production to meet growing energy demands sustainably.
Utilizing hemp for biofuel production presents numerous advantages. From its ability to grow in marginal lands to its low carbon footprint and diverse fuel options, hemp proves to be an excellent alternative to traditional fuels and contributes to a more sustainable and cleaner energy future.
Renewable Energy Source
Hemp is rapidly emerging as a promising renewable energy source, offering great potential for biofuel production. With its rapid growth cycle and high yield per hectare, hemp can be efficiently utilized to generate various types of biofuels, including biodiesel and sustainable aviation fuel (SAF).
Biodiesel, derived from hemp seed oil, is a viable alternative to traditional petroleum-based fuels. It boasts excellent mechanical properties and can be used in diesel engines without any modifications. Similarly, hemp can also be processed to produce SAF, a type of biofuel specifically designed for use in aircraft engines. SAF significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions and provides a more sustainable option for the aviation industry.
The advantages of using hemp for biofuel production are numerous. Firstly, hemp cultivation requires minimal inputs, making it cost-effective and environmentally friendly. Furthermore, hemp acts as a carbon sink, absorbing large amounts of carbon dioxide during its growth cycle. This helps to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change.
Additionally, hemp is a highly versatile crop, allowing for a variety of applications beyond biofuel production. It can be utilized in the production of construction materials, paper, textiles, and more. This versatility enhances the overall value and sustainability of cultivating hemp as a renewable energy source.
Hemp’s rapid growth cycle, high yield per hectare, and versatile applications make it an excellent option for biofuel production. Its potential to generate biodiesel and sustainable aviation fuel, along with its inherent environmental advantages, position hemp as a valuable renewable energy source with significant potential for a greener future.
High Yield Per Hectare
Hemp is known for its high yield per hectare when used for biofuel production, making it a promising crop in the renewable energy sector. On average, an acre of hemp can yield around 2.5 to 3 tons of dry biomass, which is higher than many other crops used for biofuel production.
When it comes to hemp, different components of the plant contribute to the overall biomass yield. The stems, which contain high levels of cellulose, are the main source of industrial hemp biomass. The stem particles can be converted into biofuel through various processes, such as dry distillation or anaerobic digestion. The fiber matter from the plant can also be utilized for different applications, further enhancing the overall yield.
Several factors can impact the yield of hemp biomass. The sowing density is an important factor, as it determines the number of plants that can grow in a given area. Optimal nitrogen levels in the soil are also crucial for maximizing biomass yield, as nitrogen is a key nutrient required for plant growth. The timing of the harvest is another factor that affects the yield, as harvesting the plant at the right stage ensures the highest amount of biomass.
Hemp has a high yield per hectare, outperforming many other crops used for biofuel production. Its different components, such as the stem particles and fiber matter, contribute to the overall biomass yield. Factors like sowing density, nitrogen levels, and harvest timing play a significant role in maximizing the yield of hemp biomass. This makes hemp a promising crop for biofuel production and contributes to its potential as a renewable energy source.
Potential Applications in Petroleum-Based Fuel Alternatives
Hemp shows great potential in serving as a renewable and sustainable alternative to petroleum-based fuels. Its versatility and numerous applications make it a promising contender in the quest for cleaner energy sources.
One of the key advantages of hemp in petroleum-based fuel alternatives is its ability to produce biodiesel and bioethanol. Hemp seeds, rich in fatty acids like linoleic acid, can be processed to extract hemp oil, which can be transformed into biodiesel. Hemp biomass can also be fermented to produce bioethanol. Both biodiesel and bioethanol derived from hemp have shown promising fuel properties and combustion characteristics, making them suitable options for transportation and energy production.
Furthermore, hemp’s durability and ability to thrive in lower-quality conditions also contribute to its potential as a fuel alternative. Hemp is known for its adaptability and resilience, allowing it to grow in marginal lands that are unsuitable for food crops. This not only maximizes land usage but also reduces competition with agricultural resources. Moreover, hemp can be easily stored and transported like traditional diesel, eliminating any logistical challenges associated with implementing new fuel sources.
Hemp has the potential to revolutionize petroleum-based fuel alternatives. Its ability to produce biodiesel and bioethanol, along with its durability and ease of transportation, make it an excellent candidate for a sustainable energy source. By exploring the potential applications of hemp in fuel production, we can move towards a cleaner and greener future.
Reduced Carbon Dioxide Emissions
Using hemp for biofuel production has the potential to significantly contribute to the reduction of carbon dioxide emissions. Hemp biofuel, derived from hemp oil and biomass, offers a greener alternative to traditional fossil fuels.
One of the key advantages of hemp biofuel is its ability to sequester carbon dioxide during its rapid growth cycle. Hemp plants have a remarkably fast growth rate, reaching maturity in just a few months, which allows for multiple harvests per year. As the plants grow, they absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through a process known as carbon sequestration. This means that hemp acts as a carbon sink, pulling significant amounts of carbon dioxide out of the air.
Additionally, hemp’s renewability is a key factor in the reduction of carbon dioxide emissions. Unlike fossil fuels, which release carbon dioxide when burned, hemp biofuel is carbon neutral. The carbon dioxide released during combustion is balanced by the carbon dioxide absorbed by the growing hemp plants, effectively creating a closed carbon cycle.
Furthermore, hemp plants release oxygen during their growth cycle, further enhancing their environmental benefits. This simultaneous absorption of carbon dioxide and release of oxygen makes hemp biofuel an environmentally friendly choice, helping to mitigate climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Utilizing hemp for biofuel production not only provides a renewable energy source but also contributes to reduced carbon dioxide emissions. With its rapid growth and carbon sequestration capabilities, hemp biofuel offers a sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional fossil fuels.
Versatility in Products Produced from Hemp Plant Matter
Hemp plant matter is incredibly versatile and can be utilized to produce a wide variety of useful products. The plant’s fibers can be processed to create durable and sustainable materials for construction, textiles, and paper. These hemp fibers are known for their strength and durability, making them an excellent alternative to traditional materials.
Hemp seeds are another valuable product derived from the plant matter. These seeds are rich in oil, which can be extracted and used for a variety of purposes. Hemp seed oil has numerous applications, including in cooking, beauty products, and even as a biofuel. In fact, hemp biofuel, such as hemp biodiesel, is increasingly being recognized as a viable renewable energy source that can help reduce our dependence on fossil fuels.
The chemical composition of industrial hemp is what makes it so suitable for these different uses. The plant contains a high cellulose content, which makes it ideal for fiber production. Additionally, the lignin in hemp gives it excellent tensile properties, making it strong and durable. These characteristics make hemp fibers perfect for creating construction materials, textile products, and paper.
The versatility of the products produced from hemp plant matter is truly remarkable. From fibers for construction and textiles to oil for cooking and biofuel production, hemp offers a sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional materials. Its chemical composition, including its cellulose and lignin content, further enhances its suitability for various applications.
Increased Organic Matter in Soil
One of the significant benefits of using hemp for biofuel production is its ability to increase organic matter in the soil. When hemp is cultivated for biofuel, the plant matter left after extracting the oil can be returned to the soil as organic mulch or incorporated as green manure. This organic matter acts as a natural fertilizer and helps improve the soil’s fertility.
Hemp cultivation contributes to increased organic matter in several ways. First, the leaves, stems, and other plant residues that are not used for biofuel production can be directly incorporated into the soil. As these organic materials decompose, they release nutrients and promote the growth of beneficial soil microorganisms.
Furthermore, the root system of hemp, which is extensive and highly fibrous, helps break up compacted soil and improves its structure. This allows for better water infiltration and nutrient absorption. The roots also release organic compounds and exude sugars that are food sources for soil microbes, further enhancing the nutrient cycle.
The increased organic matter in the soil provides several long-term benefits. It improves the soil’s water-holding capacity, reducing the risk of erosion and drought stress. It also enhances the soil’s nutrient-holding capacity, making essential nutrients more available to crops. Additionally, the organic matter acts as a carbon sink, helping to mitigate climate change by sequestering carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Cultivating hemp for biofuel production leads to increased organic matter in the soil, which contributes to soil enrichment and improved fertility. This nutrient-rich organic matter promotes healthier plant growth, reduces environmental impact, and supports sustainable agricultural practices.
Low Maintenance and Cost Effective Growing Process on Marginal Lands
Growing hemp on marginal lands offers several advantages due to its low-maintenance and cost-effective nature. These lands, characterized by their poor soil quality or limited access to water, are often unsuitable for conventional crops. However, hemp thrives in these conditions, making it an excellent choice for cultivation.
One of the key benefits of growing hemp material on marginal lands is its low maintenance requirements. Hemp is a hardy plant that requires minimal interventions such as fertilizer and pesticides. It has deep roots that help it access nutrients and water from the soil, reducing the need for external inputs. This not only cuts down on costs but also reduces the environmental impact associated with conventional farming practices.
Additionally, hemp has a unique ability to enhance soil nutrition. Its extensive root system breaks up compacted soil, improving its structure and allowing for better water infiltration. As hemp grows, it accumulates organic matter, which adds nutrients and improves soil fertility. This natural process eliminates the need for additional fertilizers and helps restore the health of degraded soils.
Furthermore, cultivating hemp on marginal lands can result in higher yields and lower costs compared to other crops. Its fast growth cycle and high yield per hectare make it a profitable option, even on less productive lands. Additionally, its versatility and potential applications in various industries, such as construction materials and textiles, provide additional economic opportunities.
Considering these benefits, hemp cultivation on marginal lands not only offers a sustainable solution for the use of these lands but also contributes to the production of a cost-effective and environmentally friendly biofuel source. With its low maintenance requirements, reduced fertilizer and water needs, and ability to enhance soil nutrition, hemp proves to be an excellent choice for sustainable farming and biofuel production.
Disadvantages of Using Hemp for Biofuel
While hemp shows great promise as a biofuel source, there are a few disadvantages that need to be considered.
First, hemp biofuel production is still in its early stages, which means there is limited infrastructure and technology in place to process and refine hemp into a viable fuel source. This could pose challenges in scaling up production and distribution.
Additionally, the yield of hemp biofuel per hectare is lower compared to other crops like corn or sugarcane, which means larger areas of land would be needed to produce the same amount of fuel.
Furthermore, hemp biofuel production requires significant amounts of water, which could be a concern in regions where water scarcity is already an issue.
Lastly, the cost of growing and processing hemp for biofuel is currently higher compared to traditional fossil fuels. As technologies advance and economies of scale are achieved, these disadvantages may be overcome, but for now, these factors need to be carefully considered when exploring the use of hemp as a biofuel source.
Fungal Diseases That Threaten Crop Yields
Fungal diseases pose a significant threat to hemp crop yields, thereby impacting hemp biofuel production. These diseases can cause reduced plant growth, weakened stems, leaf discoloration, and even plant death. Common fungal diseases that affect hemp plants include powdery mildew, gray mold, and damping-off.
Powdery mildew is a fungal infection that results in white powdery patches on leaves and can significantly reduce photosynthesis, leading to decreased plant vigor and biomass production. Gray mold, caused by the Botrytis cinerea fungus, attacks plant tissues, causing rot and eventually plant death. Damping-off disease, caused by various fungal pathogens, affects the germinating seeds or seedlings, causing them to rot and die before establishing a strong root system.
Preventive measures and treatments like Integrative Pest Management (IPM) are essential in hemp cultivation to mitigate the spread and impact of fungal diseases. Good practices such as crop rotation, maintaining proper spacing between plants for adequate airflow, and avoiding overhead irrigation can help reduce the incidence of fungal diseases. Additionally, applying organic fungicides or biological controls can help manage and control fungal infections.
By implementing preventive measures and treatments, hemp farmers can minimize the impact of fungal diseases on crop yields, ensuring a healthy hemp biofuel production system.
Delayed Growth Cycle Resulting in Lower Yields Initially
One of the characteristics of hemp cultivation is its delayed growth cycle, which can have an impact on initial yields. Unlike other crops that may show rapid growth early on, hemp takes time to establish a strong root system and may initially exhibit slower growth. However, this delay in growth should not deter farmers from considering hemp as a viable option for biofuel production.
While the delayed growth cycle of hemp may result in lower yields initially, it is important to note that hemp has a relatively short cropping period. In just 70-90 days, hemp can grow up to an impressive 0.31m per week. This means that despite the initial slower growth, hemp has the potential to catch up and produce significant biomass within a relatively short timeframe.
Furthermore, when it comes to biofuel production, hemp fuel offers higher yields compared to other crops. As a versatile plant, hemp can yield up to 12 tons per hectare of cellulose, 20 tons per hectare as stem particles, and 25 tons per hectare as fiber matter. This abundance of biomass makes hemp an excellent choice for biofuel production as it provides a sustainable and renewable source of raw material.
In conclusion, although hemp may have a delayed growth cycle resulting in lower yields initially, its short cropping period and ability to produce significant biomass make it a valuable option for biofuel production. The higher yields of cellulose, stem particles, and fiber matter demonstrate the potential of hemp as an efficient and sustainable resource for biofuel production.
Lower Cellulose Content Than Other Plants Used for Biofuels
Hemp, despite its numerous benefits as a biofuel crop, has a lower cellulose content compared to other plants commonly used in biofuel production. Cellulose is a crucial component in the biofuel production process as it can be broken down into sugars and subsequently fermented to produce ethanol.
The lower cellulose content in hemp plants may impact its potential use as a biofuel in a couple of ways. Firstly, a lower cellulose content means that less ethanol can be produced per unit of biomass, resulting in lower fuel yields compared to other crops with higher cellulose content. This can make hemp less economically viable for large-scale biofuel production.
To meet the growing demand for renewable energy sources, alternative biofuel crops with higher cellulose content have been explored. For example, switchgrass and miscanthus are two popular biofuel crops with significantly higher cellulose content than hemp. These crops offer the advantage of higher fuel yields per unit of biomass, making them more suitable for large-scale biofuel production.
In the biofuel production process, cellulose is critical for the conversion of biomass into liquid fuels. It is broken down through various processes such as enzymatic hydrolysis or thermochemical conversion to release sugars that can be fermented to produce ethanol. Therefore, the cellulose content of a plant plays a pivotal role in determining its viability as a biofuel feedstock.
While hemp may have a lower cellulose content compared to other biofuel crops, its other advantages, such as its short cropping period and high overall biomass yield, still make it a viable option for biofuel production. Additionally, ongoing research and advancements in technology may help improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of utilizing hemp as a biofuel feedstock.






























/5Total reviews
Persons recommended this product
Filter by
star Rating
attach_file Attachments
Anonymous
Shopper
check_circle Verified
Shop owner replied
Was this helpful
Facebook
X (Twitter)
LinkedIn
Reddit
Copied to Clipboard
Anonymous
Shopper
check_circle Verified
Shop owner replied
Was this helpful
Facebook
X (Twitter)
LinkedIn
Reddit
Copy Link
Thanks for your review!
Your feedback helps us improve our service.
There are no reviews yet.
Be the first to review “ ”
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review